How Does an Air Pressure Regulator Work?
Air pressure regulator adjusts the flow of the medium by controlling the opening degree of the opening and closing parts in the valve body, reduces the pressure of the medium, and adjusts the opening degree of the opening and closing parts with the help of the pressure behind the valve, so that the pressure behind the valve is kept within a certain range. Inside, and spray cooling water in the valve body or behind the valve to reduce the temperature of the medium, this kind of valve is called a pressure reducing and desuperheating valve. The characteristic of this valve is to keep the outlet pressure and temperature within a certain range when the inlet pressure is constantly changing. The pressure reducing valve is an essential accessory of the pneumatic control valve. Its main function is to reduce the pressure of the air source and stabilize it to a fixed value, so that the control valve can obtain a stable air source power for adjustment and control. This type of valve should generally be installed horizontally in the pipeline.
Working principle of air pressure regulator
Pilot operated pressure reducing valve
When the output pressure of the pneumatic pressure regulator valve is high or the diameter is large, and the pressure regulating spring is used to directly adjust the pressure, the spring stiffness must be too large. When the flow rate changes, the output pressure fluctuates greatly, and the structural size of the valve will also increase. . To overcome these disadvantages, pilot operated pressure reducing valves can be used. The working principle of the pilot-operated pressure reducing valve is basically the same as that of the direct-acting type. The pressure regulating gas used in the pilot-operated pressure reducing valve is supplied by a small direct-acting pressure reducing valve. If the small direct acting pressure reducing valve is installed inside the valve body, it is called an internal pilot pressure reducing valve; if the small direct acting pressure reducing valve is installed outside the main valve body, it is called an external pilot pressure reducing valve. Compared with the internal pilot-operated pressure reducing valve and the direct-acting pressure reducing valve, the air pressure regulator adds a nozzle baffle enlargement link composed of the nozzle 4, the baffle 3, the fixed orifice 9 and the air chamber B. When the distance between the nozzle and the baffle changes slightly, the pressure in the B chamber will change significantly, which will cause the diaphragm 10 to have a large displacement to control the up and down movement of the valve core 6, so that the inlet The air valve port 8 is opened large or closed small, which improves the sensitivity of the valve core control, that is, the voltage regulation accuracy is improved.
Externally piloted pressure reducing valves work on the same principle as direct-acting. There is also a small direct-acting pressure reducing valve (not shown in the figure) outside the main valve body, which controls the main valve. This type of valve is suitable for occasions with a diameter of more than 20mm, long distances (within 30m), high places, dangerous places, and difficult pressure regulation.
Direct acting pressure reducing valve with relief valve
The compressed air with the pressure of P1 is input from the left end and throttled through the valve port 10, and the pressure drops to the output of P2. The size of P2 can be adjusted by the pressure regulating springs 2 and 3. Rotate the knob 1 clockwise, compress the springs 2, 3 and the diaphragm 5 to move the valve core 8 downward, and increase the opening of the valve port 10 to increase the P2. If the knob 1 is rotated counterclockwise, the opening of the valve port 10 decreases, and P2 decreases accordingly.
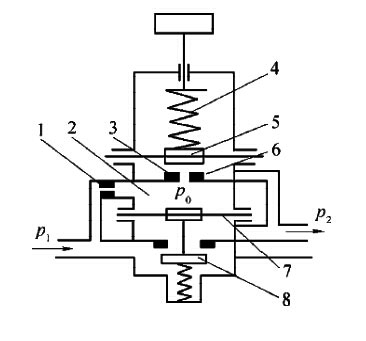
If P1 rises instantaneously, P2 will rise accordingly, so that the pressure in the diaphragm air chamber 6 will increase, and the thrust generated on the diaphragm 5 will increase accordingly. This thrust destroys the balance of the original force, making the diaphragm 5 upward When moving, a small part of the airflow is discharged through the overflow hole 12 and the exhaust hole 11 . When the diaphragm moves up, due to the action of the return spring 9, the valve core 8 also moves upward, and the intake valve port 10 is closed, the throttling effect is increased, and the output pressure is lowered until a new balance is reached, and the output pressure is basically back to the original value. If the input pressure drops instantaneously, the output pressure also drops, the diaphragm 5 moves down, the valve core 8 moves down accordingly, the intake valve port 10 is opened larger, the throttling effect is reduced, and the output pressure basically returns to the original value. Turn knob 1 counterclockwise. The regulating springs 2 and 3 are relaxed, the thrust of the gas acting on the diaphragm 5 is greater than the force of the pressure regulating spring, the diaphragm is bent upward, and the intake valve port 10 is closed by the action of the return spring. Rotate the knob 1 again, the top of the intake valve core 8 will be disengaged from the overflow valve seat 4, and the compressed air in the diaphragm air chamber 6 will be discharged through the overflow hole 12 and the exhaust hole 11, so that the valve is in a state of no output.

