What is a Mud Pump?
The term "Mud Pump" is a broad and colloquial concept for various types of pumps, and its specific application can vary depending on different regions and practices. The type of pump described in this article is largely associated with a specific type of pump used in the field of oil drilling. In fact, there are instances in which terms like "sewage pumps" and "slurry pumps," designed for non-potable water applications, may also be referred to as "mud pumps" in common usage. This blog aims to explain the mud pump as it relates to the oil drilling industry.
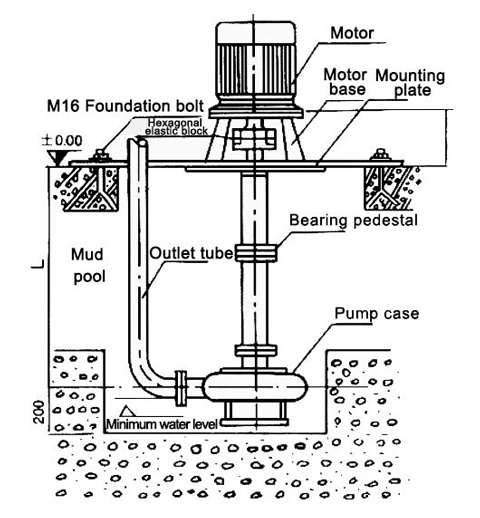
Mud pump basics
A mud pump refers to a mechanical device used in drilling to deliver mud or water-based drilling fluids into a borehole. Mud pumps are a critical component of drilling equipment.
In common circulation drilling, they are used to pressurize surface flushing media, such as clean water, mud, or polymer-based drilling fluids. These fluids are directed under a certain pressure, through high-pressure hoses, a water swivel, and the central hole in the drill pipe, directly to the bottom of the drill bit. This serves the purpose of cooling the drill bit and removing the cut rock or debris, which is then transported to the surface.
Common types of mud pumps are piston or plunger pumps, which are powered by a drive engine that rotates the pump's crankshaft. The crankshaft, through a crosshead, drives the piston or plunger in the pump cylinder in a reciprocating motion. The alternating action of the suction and discharge valves enables the pressurization and circulation of drilling fluids.
Mud pumps play a vital role in the drilling process by maintaining the flow of drilling fluids and ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of drilling operations.
Performance
The performance of a mud pump is primarily characterized by two main parameters: flow rate and pressure.
- Flow Rate: Flow rate is measured in liters or gallons per minute and is related to the diameter of the borehole and the required speed of return of the drilling fluid from the bottom of the hole. In other words, the larger the borehole diameter, the higher the required flow rate. The goal is to ensure that the drilling fluid returns from the bottom of the hole at a speed sufficient to carry away rock cuttings and fines produced by the drill bit. In geological core drilling, the desired return speed typically falls within the range of approximately 0.4 to 1.0 meters per minute.
- Pressure: The pump's pressure is determined by factors such as the depth of the borehole, the resistance in the passages through which the drilling fluid flows, and the properties of the drilling fluid being conveyed. As the depth of the borehole increases, the resistance in the piping also increases, necessitating higher pressure.
With changes in borehole diameter and depth, it may be necessary to adjust the pump's flow rate. To achieve this, the pump is equipped with a gearbox or hydraulic motor to regulate its speed. In order to accurately monitor changes in pressure and flow rate, mud pumps are equipped with flow meters and pressure gauges. This allows drilling personnel to stay informed about the pump's operation, and pressure fluctuations can help assess the condition inside the borehole, helping to prevent accidents during drilling operations.
Mud pump component

Here are the key functions and components of a mud pump:
- Circulation of Drilling Fluid: The mud pump is responsible for pumping drilling fluid (usually a mixture of water, chemicals, and clays) into the wellbore. This fluid is crucial for lubricating and cooling the drill bit, carrying cuttings to the surface, and maintaining pressure in the wellbore to prevent blowouts.
- Maintaining Pressure: Mud pumps are designed to generate and maintain high pressure within the drilling system. This pressure is essential to push the drilling fluid down the drill string, out through the drill bit, and back up to the surface, creating a continuous circulation that aids in drilling.
- Power Source: Mud pumps are powered by electric motors or diesel engines, depending on the application. These power sources drive the reciprocating pistons or plungers within the pump, creating the necessary pressure and flow of drilling fluid.
- Two Main Types: There are two common types of mud pumps: duplex (or double-acting) and triplex (or single-acting). Duplex pumps have two reciprocating pistons or plungers, while triplex pumps have three. Triplex pumps are more common due to their higher efficiency and smoother flow.
- Pressure Control: The operator can control the discharge pressure of the mud pump to match the specific requirements of the drilling operation. This pressure can be adjusted as needed to suit different drilling conditions.
- Liners and Pistons: Mud pumps have replaceable liners and pistons that come into direct contact with the drilling fluid. These components wear over time and need regular maintenance and replacement.
Mud pumps are essential equipment in drilling operations, including oil and gas drilling, water well drilling, and geothermal drilling, as they play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the borehole and ensuring the success of drilling projects. For more information go to the ATO.com.

