Freeze Dryer Working Principle
freeze dryer uses the principle of cooling and dew condensation, which is mainly composed of heat exchange system, refrigeration system and electrical control system. Compressed air first enters the pre-cooler for gas-gas or gas-water heat exchange, removing some of the thermal energy. Then it enters the hot and cold air exchanger and exchanges heat with the cold air that has come out of evaporator and cooled to the pressure dew point, which further reduces the temperature of compressed air. Compressed air then enters the evaporator and exchanges heat with refrigerant. Temperature of the compressed air drops to 0-8℃. The moisture in air is precipitated at this temperature, separated out by air-water separator, and discharged through automatic drain. The dry, low-temperature air enters the hot and cold air exchangers for heat exchange, and is output after the temperature rises.
The amount of water vapor in compressed air is determined by the temperature of compressed air. Under the condition that pressure of the compressed air is kept substantially unchanged, reducing the temperature of compressed air can reduce the water vapor content therein. Excess water vapor will condense into liquid. Freeze dryer uses this principle and adopts refrigeration technology to dry and compress air. Therefore, the freeze dryer has a refrigeration system.
Refrigeration system of the freeze dryer belongs to compression refrigeration, which is composed of four basic components: refrigeration compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve. They are connected in order by pipes to form a closed system. Refrigerant continuously circulates in the system, changes state, and exchanges heat with compressed air and cooling medium.
Refrigeration compressor draws low-pressure (low temperature) refrigerant from evaporator into the compressor cylinder. After the refrigerant vapor is compressed, its pressure and temperature increase at the same time. The refrigerant vapor with high-pressure and high-temperature is pressed to the condenser. In condenser, the higher temperature refrigerant vapor exchanges heat with the lower temperature cooling water or air. The refrigerant is condensed because its heat is taken away by water or air, and the refrigerant vapor becomes liquid.
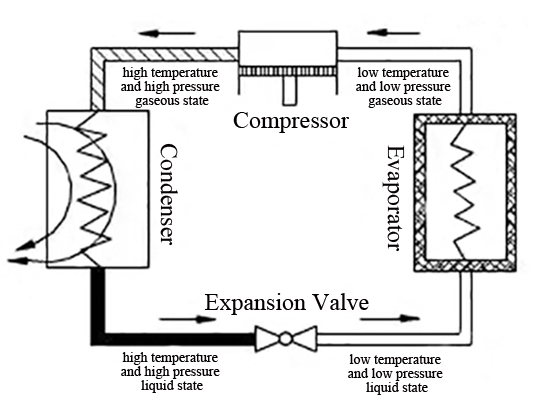
This part of liquid is then sent to expansion valve, which is throttled to a low temperature and low pressure liquid and enters the evaporator. In evaporator, the low-temperature and low-pressure refrigerant liquid absorbs the heat of compressed air and vaporizes (commonly known as evaporation). After cooling, the compressed air condenses a large amount of liquid water. Refrigerant vapor in the evaporator is sucked away by the compressor. In this way, the refrigerant passes through four processes of compression, condensation, throttling, and evaporation in the system, thereby completing a cycle.
In refrigeration system of the freeze dryer, evaporator is a device that transports cold energy. In it, refrigerant absorbs the heat of compressed air to achieve the purpose of dehydration and drying. Compressor is the heart and plays the role of sucking, compressing, and transmitting refrigerant vapor. Condenser is a device that emits heat. It transfers the heat absorbed in evaporator to the cooling medium (such as water or air) along with the heat converted by input power of the compressor. The expansion valve/throttle valve plays a role of throttling and pressure reducing to the refrigerant. In addition, it can control and adjust the amount of refrigerant liquid flowing into evaporator, and divide the system into two parts: high-pressure side and low-pressure side.
Freezing Process of Products in Freeze Dryer
When the solution is quick-frozen (decreased in temperature by 10~50℃ per minute), the crystal grains are kept at a size visible under microscope. In contrast, when slowly frozen (1℃/min), crystals formed were visible to the naked eye. Coarse crystals leave larger voids during sublimation, which can improve the efficiency of lyophilization. Fine crystals leave a small gap after sublimation, which hinders the sublimation in lower layer. Fast frozen products have fine particles, uniform appearance, good porous structure, and fast dissolving speed, so the moisture absorption of the finished product is relatively stronger.
There are two ways to pre-freeze medicines in freeze dryers. One is that the product and drying box are cooled down at the same time. The other is to cool the drying oven shelf to about -40℃, and then put the product in. The former is equivalent to slow freezing, while the latter is between quick freezing and slow freezing, so it is often used to balance lyophilization efficiency and product quality. Disadvantage of this method is that when product enters the freeze dryer, water vapor in the air will quickly condense on shelf. In early stage of sublimation, if the shelf heats up quickly, it may exceed normal load of the condenser due to the large-scale sublimation.


Freezing of the product is at a stationary state. Experience has shown that undercooling is prone to occur, causing that the product temperature has reached the eutectic point but the solute is still not crystallize. To overcome the undercooling phenomenon, freezing temperature of the product should be lower than the eutectic point, and maintain a range for a period of time until the product is completely frozen.
Working principle of the freeze dryer is based on three states of water. Water has a solid state, a liquid state, and a gaseous state. The three phases can be transformed or coexist. When water is at the triple point (temperature is 0.01℃ and water vapor pressure is 610.5Pa), water, ice, and water vapor can coexist and balance each other. In high vacuum state, use the sublimation principle to make the water in pre-frozen material not going through ice melting, directly as an ice state sublimate to water vapor and then remove it, so as to achieve the purpose of freeze drying.
After freeze-drying by the freeze dryer, the products are spongy, no shrinkage, excellent rehydration, and low water content. After corresponding packaging, they can be stored and transported at normal temperature for a long time. Since freeze dryers have unparalleled advantages compared with other drying methods, this technology has become more and more popular since its inception, and has been increasingly used in medicine, biological products and food. Most of the biological products such as serum, bacteria, Chinese and western medicine are biologically active substances. Freeze-drying technology also provides a good solution for preserving biological activity.

