Carbon Dioxide Sensor Basics: Working Principle, Maintenance and Advantages
A carbon dioxide sensor or CO2 sensor is an instrument for the measurement of carbon dioxide gas. The most common principles for CO2 sensors are infrared gas sensors (NDIR) and chemical gas sensors. Measuring carbon dioxide is important in monitoring indoor air quality, the function of the lungs in the form of a capnograph device, and many industrial processes.

How does CO2 sensors work?
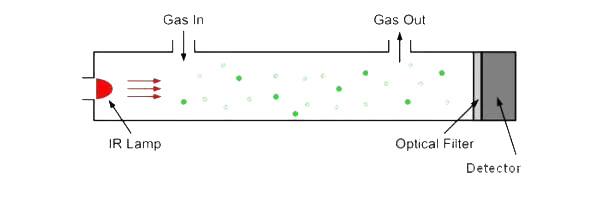
NDIR CO2 sensors monitor and detect the presence of carbon dioxide based on the absorption of specific wavelengths of infrared light. NDIR sensors include infrared sources, lamps, bandpass filters, and detectors. The target gas is determined by filter wavelength selection. For CO2, the most commonly used wavelength is 4.26 µm. This wavelength is simply not absorbed by other common gases or water vapor, greatly reducing cross-sensitivity and effects on moisture and humidity.
Normal operation of an NDIR CO2 sensor involves pumping or diffusing gas into a light pipe. The electronics then measure the absorption of characteristic wavelengths of light. The amount of light absorption is converted to an electrical output that provides parts per million (ppm) or % volume measurements. In short, more light absorbed means more target gas molecules are present, which results in a lower output signal and a higher reported CO2 concentration.
How to maintain a carbon dioxide sensor?
- The CO2 sensor should be regularly maintained, do not drop it, and do not let the instrument inhale dust.
- When the carbon dioxide sensor is not in use for a long time, the power supply of the instrument should be turned off, and it should be stored carefully and protected from moisture and dust.
- The model, specifications and parameters of the components in the original circuit shall not be changed during maintenance, and the original package shall not be changed. All repairs must be carried out on the well by professionals.
- Alarm silently for poor contact or circuit failure, check solder joints, wires and circuits.
- The maintenance and maintenance of the carbon dioxide gas sensor should regularly adjust and maintain the alarm device, and the adjustment period should not exceed 15 days.
- In the normal use of the CO2 gas sensor, during the effective service life of the sensor, the NDIR CO2 sensor should be calibrated and checked regularly every 6 months or 1 year to ensure accurate and effective gas monitoring. The sensor must be replaced.
3 Benefits of Using CO2 Sensor
By collecting and analyzing monitoring data from CO2 sensors, they can quickly and efficiently identify potential CO2 accumulation in their offices and indoor spaces. Combining sensors with demand-controlled ventilation (DCV) will automatically adjust airflow within an office in response to carbon dioxide levels at any given time. This both provides a better working environment and saves energy as the ventilation system only operates when needed.
The three main benefits of using sensors to measure carbon dioxide levels and ventilate accordingly are:
- A healthy and safe working environment with carbon dioxide levels controlled within the acceptable and healthy range below 1000 ppm.
- Increased productivity as the effects of elevated carbon dioxide levels on cognitive skills are mitigated.
- Energy saving through optimal use of ventilation system.

