What is a Vane Air Motor?
The vane air motor is a power device with compressed air as the working medium. It uses the expansion effect of compressed gas to convert pressure energy into mechanical energy and is widely used in industrial production. In order to let you know more about the vane air motor, we will bring you knowledge about the definition, structure, and principle of the vane air motor.
The structure of the vane air motor
A vane air motor is one of the classifications of air motors, mainly composed of a stator, rotor, blades, and housing. The number of blades depends on the power and efficiency of the motor, usually 4, 6, or 8.
There are long slots on the rotor, and the blades are housed in the slots. The stator has air distribution slots for air intake and exhaust, and there are sealing covers at both ends of the stator. The rotor and stator are mounted eccentrically. In this way, the blades sliding in the radial direction and the inner cavity of the casing constitute the working chamber of the air motor.
Compared with electric motors, air motors can rotate faster, usually reaching more than 3000rpm, and even small vane air motors can reach speeds of 20000rpm.
How do vane air motors work?
Vane air motors generally have two holes, one for air intake and one for exhaust, and the two holes can be interchanged to achieve forward and reverse rotation, and the direction can be easily controlled by using an ordinary control valve. The compressed air enters the inner cavity of the motor through the air inlet, and the pressure generated acts on the blades, which drives the rotor to rotate through the blades, thereby driving the equipment to run through the output shaft. The vanes are positioned through the vane slots on the inner wall and the rotor so that they can only move in the vane slots to achieve the sealing effect.
Compressed air is input from hole A, and a small part of the gas pushes the vanes out through the vane grooves of the sealing covers at both ends of the stator so that the vanes are close to the inner wall of the stator. Because the extension length of the two blades is different, there is a torque difference, which causes the blades and the rotor to rotate in the counterclockwise direction, and the compressed gas is finally discharged from hole B on the stator. If you change the input direction of compressed air (i.e. compressed air enters from hole B and leaves from hole A), you can change the rotation of the rotor.
The vane air motor adopts the structural form of maintaining the expansion stroke of compressed air. When the rotor turns to the position of exhaust port C, the compressed air in the working chamber is exhausted once, and then the rest of the compressed air continues to expand until the rotor turns to the position of output port B for secondary exhaust. Adopting this structure can effectively utilize the energy when part of the compressed air expands to increase the output power.
Work process
First, the compressor puts air at high pressure through volumetric compression of the rotor or piston, which is then fed into the air motor. The rotor rotates on a shaft protruding from the housing. Therefore, an instrument powered by an air motor can gain kinetic energy by connecting to this shaft.
The gap between the rotor and the casing is divided by vanes. The center of the rotor is slightly offset from the center of the housing, so the small spaces separated have different volumes. Not only does the compressed air create the blowing pressure, but the force of this pressure differential is transmitted from the high-pressure chamber to the medium/low-pressure chamber, causing the vane rotor to spin at incredible speeds. Vane air motors are generally less costly than high-precision motors and output hydraulic motors (although compressors etc. need to be used separately), but air motors do not risk flying sparks even when overloaded.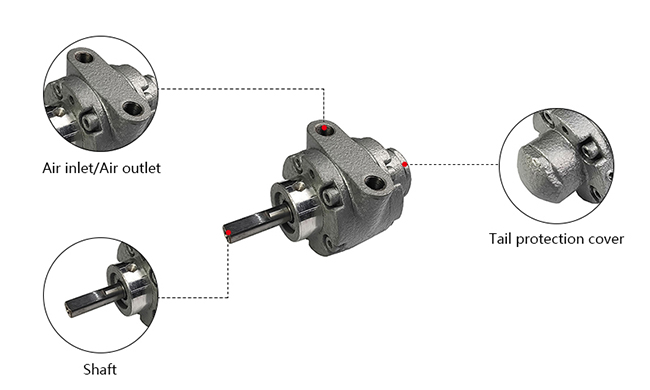
Air vane motor features
- Large power range and speed range. The power ranges from a few hundred watts to tens of thousands of watts; the speed can range from zero to 10,000 revolutions per minute.
- Easy to operate and easy to maintain. The vane air motor has the advantages of simple structure, small size, lightweight, high horsepower, and convenient maintenance.
- Using air as the medium, there is no difficulty in supplying, and there is no need to deal with used air. The pollution-free compressed air can be put into the atmosphere for centralized supply and long-distance transportation.
Application range
600w vane air motors are generally used in the range of medium and small capacity and high-speed rotation and are mainly used in pneumatic tools, high-speed rotating machinery, and mining machinery. Its air consumption is larger than that of the piston type, its output power is 0.1-20kW, and its speed is 500-25000r/min. In addition, when the vane air motor starts and runs at a low speed, it must be equipped with a deceleration mechanism when the speed is below 500r/min.
- Power drive, high torque drive, high-speed drive.
- Cutting processing (drilling, milling, tapping, grinding, polishing, chamfering, deburring, etc.).
- Assembly (tightening assembly, packaging, riveting, etc.).
- Can be used in various machines and machinery:
Printing, packaging machinery, capping machines, food and beverage machinery, filling machines, machine tools, pipe dredging machines, machines for flammable and explosive environments, mixers, beveling machines, balers, pumps, blowers, hoists, winches, valve drives, mobile platforms, material handling lines, assembly tightening units, conveyor belts, indexing tables, cutting, wind saws, tapping machines, ships, woodworking, petroleum, mining, paper, petrochemical machinery, etc.
It can be used with various functional mechanisms:
Propulsion mechanism, numerical control system, positioning system, robot or manipulator, speed control system, various sensors, various accessories, and various functional components.

