How Does a Star-Delta Starter Work for 3-Phase Induction Motors?
Star-delta starters are widely used in industrial motor control systems to optimize the startup performance of high-power three-phase induction motors. By controlling the motor’s connection mode during startup and normal operation, they effectively reduce inrush current and mechanical stress, ensuring smoother acceleration and more stable system operation.
This article provides a comprehensive explanation of the working principle of a star-delta starter, along with a detailed wiring method, key operational advantages, and typical industrial applications, helping readers gain a clear and practical understanding of this widely adopted motor starting solution.

Contents
Introduction
When operating 3 phase induction motors with power ratings above 7.5 kW, direct-on-line (DOL) starting can result in excessive starting current and mechanical stress. To address this issue, the star-delta starter is commonly employed.
This starting method combines star and delta configurations to significantly reduce starting current and torque during motor startup. As a result, it minimizes electrical and mechanical stress, improves operational stability, and extends motor service life.
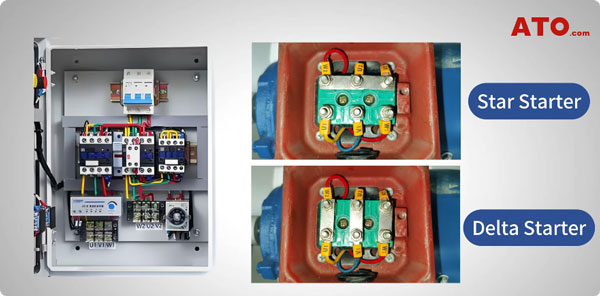
Working Principle
The star-delta starter operates by initially connecting the 3 phase induction motor windings in a star configuration, which reduces the phase voltage applied to the motor. Once the motor reaches a certain speed, the connection is switched to delta configuration, allowing full-line voltage operation for normal running conditions.
This transition ensures a smooth startup process while maintaining efficient performance during steady-state operation.
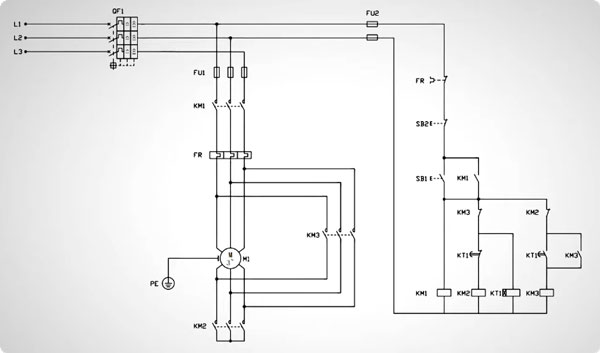
Detailed Wiring Procedure
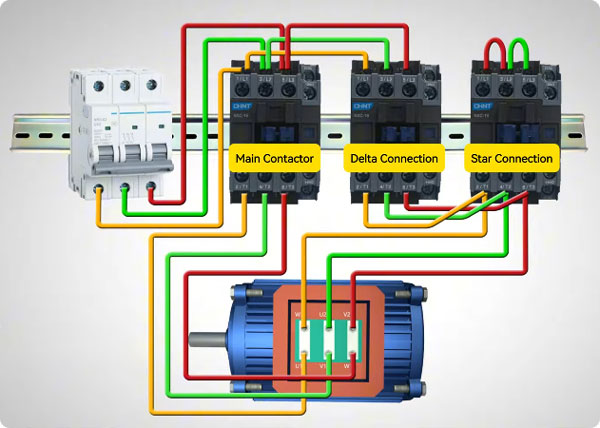
- Power Connection
The wiring process begins by connecting the three-phase power supply from the circuit breaker to the main contactor (KM1). From there, the power lines are connected to the motor terminals U1, V1, and W1, allowing the main contactor to control the motor’s power supply. - Star Connection for Reduced-Voltage Starting
A second contactor, known as the star contactor (KM2), is introduced to establish the star connection during startup. The upper terminals of this contactor are shorted together, while the lower terminals are connected to the motor terminals W2, U2, and V2.
When both the main contactor and the star contactor are energized simultaneously, the motor windings are connected in a star configuration. This reduces the voltage applied to each winding, resulting in lower starting current and smoother motor acceleration. - Transition to Full-Voltage Delta Operation
After the 3-phase induction motor completes its initial acceleration phase, it must transition to full-voltage operation for optimal performance. This is achieved by engaging the delta contactor (KM3).
In the delta configuration, the upper terminals of the delta contactor are connected to the main contactor, while the lower terminals are linked to the star contactor terminals. When the main contactor and delta contactor are engaged together, the motor windings are reconfigured into a delta connection, enabling full-line voltage operation.
To ensure safe operation, proper electrical and mechanical interlocking must be implemented to prevent the star and delta contactors from being energized at the same time. In most systems, a timer is used to control the delay between star disconnection and delta engagement. - Operational Sequence Summary
During startup, the main contactor (KM1) and star contactor (KM2) are energized simultaneously, allowing the 3-phase induction motor to start under reduced voltage and current conditions. Once the motor reaches a predetermined speed, the star contactor disengages. After a short delay, the delta contactor (KM3) is energized, switching the motor to delta configuration for normal operation.
This controlled transition ensures smooth acceleration and reliable long-term performance.
Benefits
The star-delta starter provides several key advantages in industrial motor applications:
- Reduced starting and inrush current, minimizing stress on the power supply
- Lower voltage dips during startup, improving system stability
- Reduced thermal and mechanical stress on motor windings
- Enhanced 3-phase induction motor efficiency and extended service life
- Effective coordination between control circuitry and motor operation
Applications
Star-delta starters are particularly well-suited for applications where low starting torque is sufficient and reduced-voltage starting is required, helping to limit inrush current and reduce mechanical stress on the 3-phase induction motor and connected equipment. Typical use cases include centrifugal compressors, pumps, fans, and blowers, as well as other industrial machinery that operate under low starting torque conditions. By providing a smoother and more controlled startup, star-delta starters not only protect the motor and associated equipment but also improve overall system reliability and efficiency in industrial operations.

Conclusion
The star-delta starter is a proven and reliable method for controlling the startup of three-phase induction motors. By understanding its working principle, wiring procedure, and application scenarios, engineers and technicians can effectively optimize motor performance while reducing electrical and mechanical stress.
Mastering the use of star-delta starters is a key step toward building efficient, durable, and well-coordinated motor control systems. For more technical guidance, wiring diagrams, and motor control solutions, visit the ATO.com to explore a wide range of industrial automation products and resources.

