How to Calibrate Conductivity Sensor?
The calibration of conductivity sensor is the key operation to ensure the measurement accuracy. Its core is to correct the measurement deviation of the sensor through the standard solution of known conductivity. The following are common calibration steps, which are suitable for laboratory and industrial online sensors.
- Before Calibration
- Calibration Mode Startup and Parameter Setting
- Step-by-step Calibration Operation
- After Calibration
- Questions and Precautions
Before Calibration
1. Prepare tools and materials
Standard solution: Select at least 2 concentrations of standard solutions according to the measurement range of the conductivity sensor.
Container: Clean glass or plastic beaker.
Auxiliary tools: Thermometer (used when calibrating temperature compensation), pipette (pipetting standard solution), distilled water or deionized water (cleaning electrodes), dust-free cloth or filter paper (absorb the moisture on the electrode surface, and do not wipe the sensing surface of the electrode).
Equipment: Conductivity sensor host (connected controller/ transmitter) to ensure that the power supply is stable and the calibration mode can be started normally.
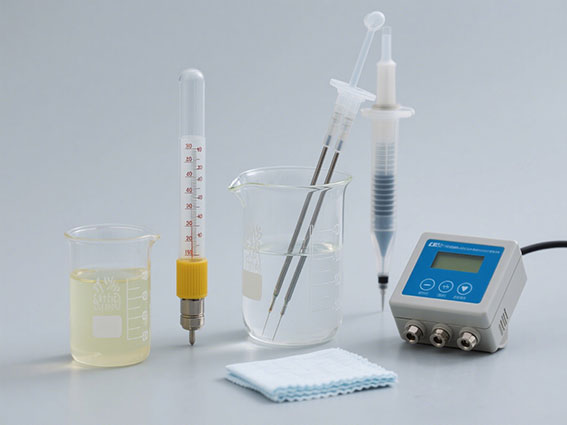
2. Preprocess conductivity sensor and standard solution
Clean the conductivity sensor: Rinse the electrode surface with distilled water 3 to 5 times to remove residual pollutants. If there are stubborn stains, you can lightly brush with a soft-bristle brush or (10%) soak for 5 minutes and then rinse (to avoid scratching the electrode coating).
Equilibrium temperature: Pour the standard solution into the beaker, place it in room temperature environment with the sensor for 10 ~ 15 minutes, ensure that the temperature of the standard solution is consistent with that of the sensor (reduce the temperature compensation error), and record the current temperature of the standard solution (or use the temperature probe that comes with the conductivity sensor).
Calibration Mode Startup and Parameter Setting
1. Enter calibration mode
- Turn on the conductivity sensor host or connected controller, and enter the "Calibration Menu" according to the instructions (usually select the "Calibration" or "Calibration" option through the button or software interface).
- Select calibration type: Most sensors support "single-point calibration" (suitable for daily fast calibration) and "multi-point calibration" (suitable for high-precision requirements). It is recommended to give priority to multi-point calibration.
2. Set the calibration parameters
- Enter the conductivity value of the standard solution (Note: the standard solution label usually marks the theoretical value at 25 °C. If the actual temperature deviates from 25 °C, it needs to be corrected according to the temperature coefficient of the standard solution, some smart conductivity sensors can automatically correct).
- Select the number of calibration points.
Step-by-step Calibration Operation
1. The first point of calibration
- Immerse the cleaned electrode in the standard solution, ensure that the electrode sensing surface (usually the electrode sheet or annular area) is flooded, and avoid touching the wall or bottom of the beaker.
- Wait for the reading to stabilize (usually 30 ~ 60 seconds, the screen shows "stable" or the value fluctuates < ± 1%).
- Press the "Confirm" key, the instrument will record the deviation between the conductivity sensor measurement value and the theoretical value of the standard solution, and automatically calculate the correction coefficient.
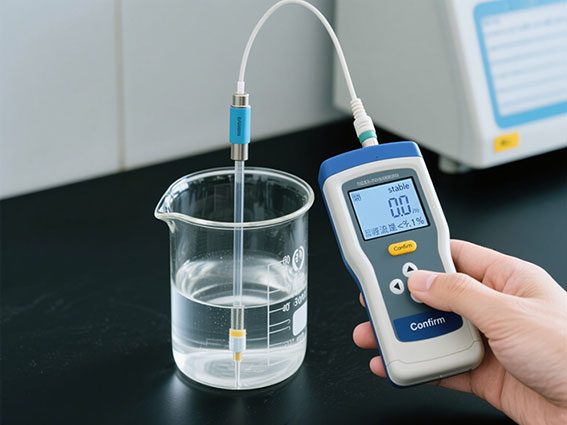

2. The second point of calibration
- Take out the electrode, rinse it 3 times with distilled water, and absorb the surface water with filter paper (to avoid contaminating the high-concentration solution with the residual low-concentration standard solution).
- Repeat the above steps: Immerse in the second standard solution, wait for stability and confirm. The instrument will optimize the linear correction curve based on the two-point data to reduce the full-scale error.
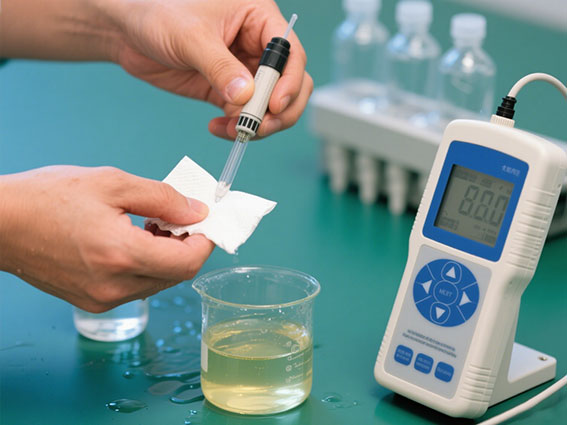

3. Calibration verification
- After the calibration is completed, the standard solution can be measured again to check whether the deviation between the displayed value and the theoretical value is within the allowable range (usually within ± 2%).
- If the deviation is too large, it is necessary to re-clean the electrode and repeat the calibration to eliminate operation errors.
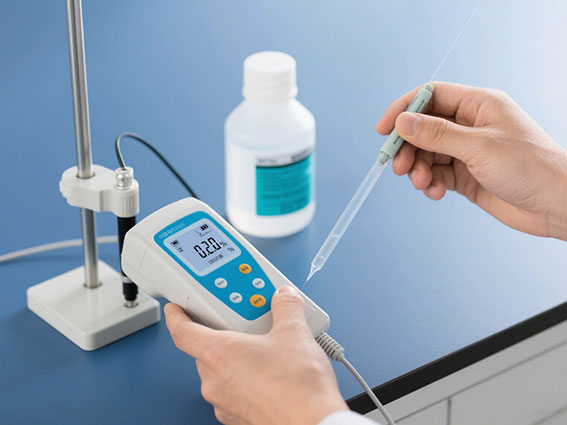

After Calibration
1. Save and record data
- Confirm that calibration parameters have been saved to the conductivity sensor or host.
- Record the calibration date, standard solution information, and deviation value before and after calibration as a reference for the next calibration (it is recommended to attach it to the equipment maintenance log).
2. Clean conductivity sensors and tools
- Rinse the electrode with distilled water. If it is not used for a long time, it must be stored according to the instructions (for example, the metal electrode can be soaked in 3mol/L KCl solution to avoid drying and aging of the electrode).
- If the standard solution is not contaminated, it can be sealed and stored in refrigeration (short-term use). If it is contaminated or expired, it should be discarded (to avoid affecting the next calibration).
Questions and Precautions
Calibration failure: If the conductivity sensor prompts "calibration error", it may be electrode contamination (re-cleaning), standard solution failure (replacement with new solution), or electrode damage (such as electrode sheet falling off, electrode needs to be replaced).
Electrode constant drift: After long-term use, the electrode constant K may change due to corrosion or wear. The core of calibration is to correct the K value to ensure the accuracy of the measurement formula (conductivity = K × current/voltage).
Special sensors: The calibration steps of four-electrode sensors or inductive sensors are similar. For inductive sensors, you need to pay attention to the uniformity of the standard solution (to avoid bubbles affecting electromagnetic field induction). Through regular standardized calibration, it can effectively counteract the performance attenuation of the sensor and ensure the reliability of measurement data.
Summary
Regular and standardized calibration is a critical measure to ensure the long-term measurement accuracy of conductivity sensors. By employing multi-point calibration, temperature compensation, and strict cleaning procedures, it effectively corrects electrode constant drift and systematic errors, eliminating measurement deviations caused by sensor aging, contamination, and environmental changes. Post-calibration steps such as verification, documentation, and proper storage are essential to establish a complete quality traceability chain, ultimately providing reliable and continuous data support for laboratory testing and industrial online process control. If the conductivity sensor cannot be calibrated correctly, it is recommended to contact ATO automation store or the relevant technical personnel.

