How Rain Sensor Works in Car?
Smart Rain Sensors: Enhancing Driving Safety & Comfort
Today, more and more cars are equipped with intelligent rain sensors, making driving in the rain safer and more convenient. With the advancement of intelligent automotive technology, rain sensors are addressing this challenge. They monitor rainfall conditions in real time and automatically adjust wiper speed, optimize headlights, and even interact with the sunroof system, ensuring a clear view even in inclement weather. This article will explore the operating principles, intelligent features, and how rain sensors enhance the driving experience, showcasing the remarkable advancements in modern automotive technology for safety and comfort.
Rain sensors are widely used in intelligent driving systems, with automatic wipers already having a significant presence in most automotive applications. Car rain sensors used to control windshield wiper speed and frequency not only improve comfort but also enhance driving safety. The correct wiper speed ensures good visibility through the car's windows in all weather conditions. Automakers consider the rearview mirror as an ideal location for rain sensors, which can also be installed in cameras, sun sensors, and ambient light sensors.

How Car Rain Sensors Work?
The main function of a rain sensor is to detect the presence and intensity of rain. When driving in inclement weather such as rain or snow, the sensor sends a signal to a microcomputer. The microcomputer then intelligently adjusts the headlight beam width, distance, and brightness to ensure a clear view for the driver. Furthermore, the sunroof system automatically closes the windows when rain is detected, further ensuring driving safety.
To ensure clear vision in the rain, cars are equipped with automatic windshield wipers. When sensors detect raindrops hitting the windshield, they immediately command the wipers to move, clearing the water droplets from the glass. Simultaneously, an intelligent control system continuously monitors and analyzes the wiper frequency, aiming to enhance the driver's vision and ensure an unobstructed view, thereby ensuring safe driving. Conventional cars are typically equipped with only three wiper speeds: slow, medium, and fast. However, these three speeds are sometimes insufficient when driving in the rain. Slow speed may not be fast enough, while fast speed may be too fast. However, a rain sensor solves this problem. A high-precision rain sensor monitors the amount of rain on the windshield in real time and automatically adjusts the wiper speed to ensure a clear view at all times.
There are two types of rain sensors commonly used in cars: optical rain sensors and capacitive rain sensors.
Optical Rain Sensors Works in Car
An optical rain gauge is a commonly used rain sensor that measures rainfall using optical principles. The working mechanism of an optical rain gauge can be simply summarized as follows: it detects the presence of raindrops by emitting a light beam and receiving scattered light, and calculates rainfall based on the number and size of raindrops. The core components of an optical rain gauge are a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits a light beam that propagates through the air. When the light beam encounters raindrops in the air, some of the light is scattered by the raindrops and propagates in different directions. The receiver, located opposite the transmitter, receives and analyzes the scattered light signal. The receiver measures the intensity or other characteristics of the scattered light that returns, such as intensity variations and time delays. These characteristics can be used to determine the presence, number, and size of raindrops.
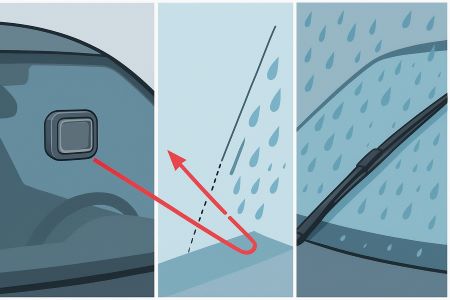
The working principle of an optical rain gauge is based on the properties of scattered light. When a light beam encounters raindrops, the raindrops scatter the beam and change its direction of propagation. The larger and more numerous the raindrops, the greater the intensity and delay of the scattered light. Therefore, by measuring the characteristics of the scattered light, the presence and amount of raindrops can be inferred.
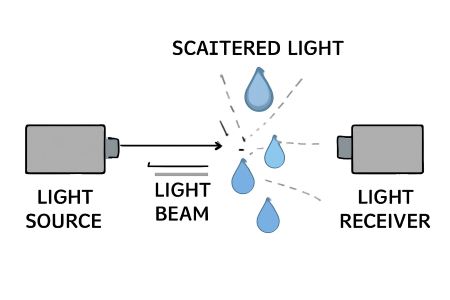
To ensure accurate measurements, optical rain gauges typically utilize a combination of multiple transmitters and receivers. This allows for more data and reduces errors.
Optical rain gauges offer many advantages, including sensitivity to rainfall intensity, a wide measurement range, and fast response times. They can monitor precipitation in real time and provide accurate rainfall data. Consequently, they are widely used in fields such as meteorology, water resource management, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. The cost-effective optical rain sensor sold in the ATO online store is a good choice. It uses the internal optical sensor principle to measure rainfall, supports RS485 output and pulse output, has a long transmission distance and stable signal.
Capacitive Rain Sensors Works in Car
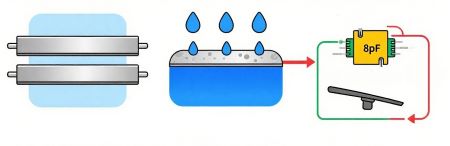
Capacitive rain sensors can be considered the key technology for intelligent windshield wiper control. This sensor cleverly exploits the difference in dielectric constant between water and glass. Engineers place parallel, finger-shaped metal plates between the inner and outer layers of the windshield. In dry conditions, a dielectric constant forms between the windshield's outer surface and the metal plates. However, when rain falls on the glass, the situation changes. The windshield's dielectric constant varies with the amount of water on the glass. Capacitive sensors can keenly detect this change in dielectric constant and thus detect the presence of rain. To maximize the sensitivity of capacitive sensors, they are typically mounted on the windshield's surface or closely attached to the lower surface. However, if mounted on the outer surface, the metal coating may be scraped off due to prolonged wiper operation. While capacitive sensors have high sensitivity and fast response, long-term use can affect detection accuracy due to mechanical wear of the wipers or contamination on the glass surface, requiring regular maintenance and calibration.
Summary
These operating principles of windshield wipers are undoubtedly the fruit of advanced automotive technology. They act as the vehicle's "eyes," allowing the car to "see" the rain and automatically and precisely adjust wiper operation. This not only brings great convenience to the driver, eliminating the need for frequent manual wiper operation while driving, allowing them to focus more on the road, but also ensures a clear view of the windshield at critical moments, such as during a downpour or a gentle drizzle, ensuring driving safety and making every journey more secure and comfortable.

