PWM Speed Control for Brushless DC Motors
When it comes to modern motion control, precision and efficiency are critical. One of the most effective techniques for achieving both is Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). In this blog, we will explore how PWM works to regulate the speed of Brushless DC (BLDC) motors, why it is essential for their efficient operation, and where it is commonly applied.
1. Importance
Brushless DC (BLDC) motors consist of a rotor equipped with permanent magnets and a stator containing windings. These motors operate based on electronic commutation, wherein the controlled energization of the windings generates a rotating magnetic field. This magnetic interaction drives the rotation of the rotor.
BLDC motors typically incorporate a three-phase design, requiring each phase to be energized in a precise sequence to achieve continuous and controlled motion. This process, known as the commutation sequence, necessitates the use of a dedicated controller. The controller determines the exact order in which the stator windings are energized. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) serves as the underlying control mechanism, providing the necessary regulation for accurate and efficient motor operation.
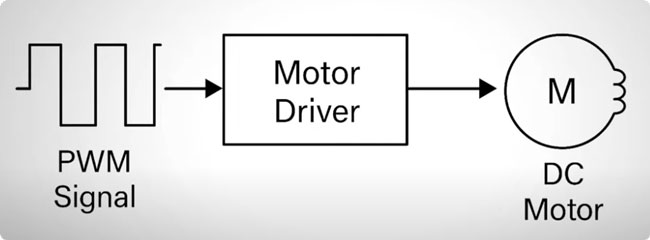
2. Principle
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a widely used technique for regulating the speed of Brushless DC (BLDC) motors. This modulation method operates by varying the width of the electrical pulses within a control signal while maintaining a constant frequency. The technique involves rapidly switching the voltage supplied to the motor on and off, where the duration of each "on" pulse relative to the total signal period determines the effective output.
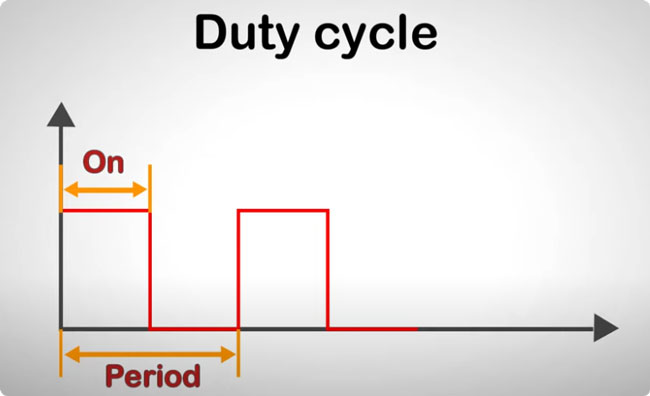
In PWM-based speed control systems, the duty cycle—defined as the ratio of pulse-on time to the total signal period—dictates the average voltage delivered to the motor windings. A higher duty cycle increases the average voltage applied to the motor, resulting in greater rotational speed. Conversely, reducing the duty cycle lowers the average voltage, thereby decreasing motor speed.

By adjusting the duration of voltage application to the motor windings, PWM enables precise and efficient speed regulation in BLDC motors. Fundamentally, PWM functions as an electronic switch that rapidly cycles power to the motor coils at varying intervals. This switching action effectively controls the strength of the magnetic field generated by the stator, which in turn governs the rotational speed of the rotor. In practice, this modulation is carried out by BLDC Motor Controllers, which generate the required PWM signals to ensure accurate and stable motor operation.
3. Benefits
In the realm of electric motor control, brushless DC (BLDC) motors extensively utilize Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) for speed regulation due to its exceptional precision, efficiency, and adaptability. PWM serves as a fundamental technique that meets the critical demands of modern motor applications through the following key advantages:
Precise Speed Control: PWM enables fine adjustment of the average voltage supplied to the motor windings by modulating the duty cycle—the ratio of pulse-on time to the total signal period. This allows accurate speed control across a wide range, from very low to high RPMs, ensuring the motor operates exactly as required.
Efficiency and Heat Management: Unlike linear regulation methods, which suffer from significant power dissipation, PWM minimizes energy loss by rapidly switching transistors between fully on and off states. Power is delivered only during the "on" phase, reducing wasted energy and heat buildup. This efficient power management helps BLDC motors maintain peak performance while extending operational life.
Smooth Operation: The high-frequency switching of PWM creates an effectively constant average voltage, resulting in smooth torque output and minimal vibration or audible noise. This leads to stable motor rotation without sudden speed variations, reducing mechanical stress and improving overall system reliability.
Dynamic Response: PWM facilitates rapid adjustments to motor speed in response to fluctuating loads or control signals. This dynamic capability allows BLDC motors to adapt instantly to changing operational demands, making them suitable for applications requiring high responsiveness.
Flexibility: Operators can easily tailor motor performance by adjusting the PWM duty cycle, enabling precise tuning to meet diverse application needs. This flexibility makes PWM ideal for use across industries—from robotics to HVAC systems—where varying speed settings are essential.
Compatibility & Easy implementation: Most modern microcontrollers and motor drivers feature built-in PWM functionality, simplifying system design and reducing development time. Furthermore, PWM can be seamlessly incorporated into closed-loop control systems using feedback from encoders or Hall effect sensors, enabling real-time adjustments that enhance accuracy under varying conditions.
4. Applications
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) speed control is extensively employed in brushless DC (BLDC) motor applications across a diverse range of industries, including:
- Robotics: Smooth, responsive motion for articulated joints.
- Automotive systems: Electric power steering, fans, and pumps.
- HVAC systems: Efficient airflow and temperature regulation.
- Aerospace: High-performance actuation with minimal energy waste.
In all these fields, PWM ensures tailored performance while optimizing energy usage.

5. Conclusion
In summary, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) serves as a foundational technique for speed control in Brushless DC (BLDC) motors, delivering precise regulation and enhanced operational performance. Its implementation results in significantly improved energy efficiency, reduced thermal output, and smooth, stable motor operation. The method also supports dynamic responsiveness to load variations and offers considerable flexibility in control adjustments. Furthermore, PWM is highly compatible with modern electronic systems and straightforward to implement. These collective advantages establish PWM as an indispensable strategy for maximizing BLDC motor performance across diverse industrial and commercial applications.
If you still have any questions about PWM Speed Control for Brushless DC Motors, feel free to reach out to the ATO store. Their professional team will be glad to provide expert guidance and tailored solutions for your specific needs.

